Is Jaggery The Alternative To Sugar You Were Looking For?
Blogs16 Jun 2025
IN THIS ARTICLE
Jaggery or Gur as it is called in India is a natural sweetener that many of us use regularly in our daily chai, coffee and food. Jaggery is made with the juices of palm trees and sugarcane and is popular in the Asian and African regions. It makes for a delicious sweet addition to several dishes and has a distinct flavour which is similar to brown sugar and molasses. You can find jaggery in solid, liquid and granular forms.
In this article, we’ll explore Jaggery, its nutritional profile, some important jaggery benefits and if it could be a healthier sugar alternative.
What is Jaggery?
Jaggery is a solid or semi-solid by-product of processing or boiling the sweet juices of palm trees and/or sugarcane. It’s known to have a sweet, wine-like flavour and contains some vitamins and minerals, salts, iron and fibre. Organic jaggery typically contains these nutrients while being free of chemicals and artificial ingredients. Conversely, white sugar is just crystalline form of sucrose without any of these nutrients. This is why it’s a popular choice among health-conscious people who are looking for sugar substitutes.
Jaggery Nutritional Profile
Jaggery contains a host of nutrients depending on the type you choose. The benefits of eating jaggery can be mapped to some of the nutrients it contains. Jaggery is a source of essential minerals such as Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Potassium, and Phosphorus. It is also a source of Vitamin A, D, E, C etc.
Jaggery is also known as ‘medicinal sugar,’ as it is often used in the making of pharmaceuticals. However, jaggery is high in calories and sucrose so you must practise moderation when consuming this natural sweetener.
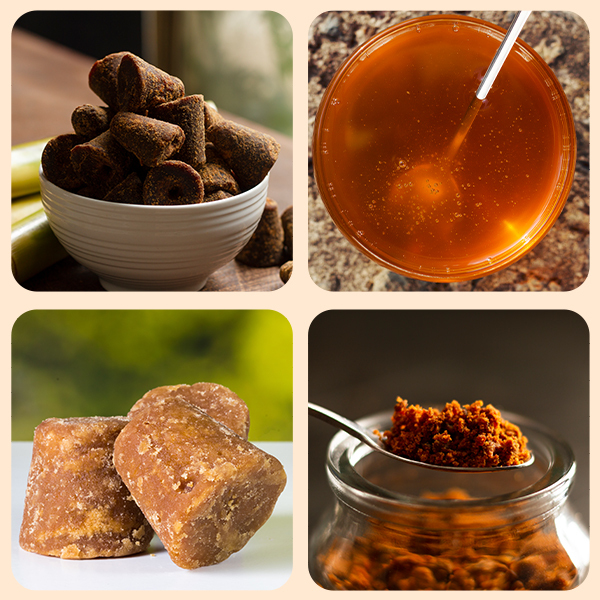
Forms of Jaggery
Solid Jaggery:
When the clarified sugarcane juice is heated and stirred in open pans, concentrated masses are formed, known as solid jaggery. This product can be turned into any desired shape or size which makes it convenient to store and use. Similarly, sap collected from palm trees is also boiled, condensed and crystallised to form solid jaggery.
Liquid Jaggery:
Liquid jaggery is made as a by-product of the concentration of sugarcane juice or palm tree sap. It’s a semi-liquid syrup that is popularly used in Maharashtra, and West Bengal.
Granular Jaggery:
When a wooden scraper is used on the concentrated sugarcane juice, it forms grains. This, when cooled down, forms granular jaggery.
Organic Jaggery:
Unlike regular jaggery which contains some chemicals such as Sodium Bicarbonate, sulphur dioxide, citric acid etc., organic jaggery is chemical-free and can be made only through specific varieties of sugarcane and palm trees.
Is Jaggery better than sugar?
Jaggery and sugar have different compositions. White sugar is solid granules of sucrose, and Jaggery is a golden brown syrup or solid which contains mineral salts, iron and some fibre. White sugar is absorbed readily by our body, whereas jaggery is digested slowly which means that the energy released is also slower.
Since jaggery contains a high amount of potassium, it may help with preventing water retention and weight management, unlike white sugar which is known to increase weight. Additionally, the consumption of white sugar has been tied to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions.
Since jaggery is seemingly healthier than sugar because of the presence of added minerals, it is looked at as the best replacement for sugar when consumed in moderation. In reality, jaggery offers more health benefits than white sugar, however, jaggery itself does contain sucrose and a high amount of calories which means that it must be had in moderation. Those with diabetes must refrain from consuming jaggery as the best substitute sweetener and speak with their physician before using it.
Jaggery Usage
If you want to switch your white sugar with jaggery, you can mix a one teaspoon of it in your tea or coffee. You can use it in drinks, sweets and other dishes too. However, keep in mind that jaggery is still a form of sugar, so make sure you have this sugar alternative in small quantities only.
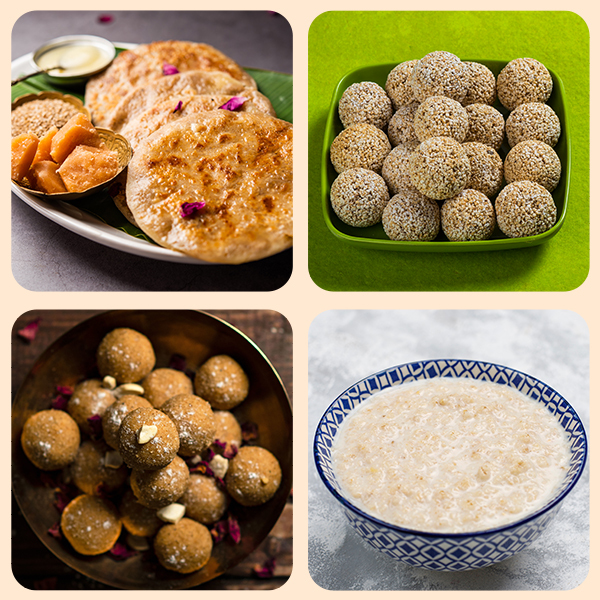

Some popular dishes made with jaggery or Gur are Jaggery roti, Til Gur Ke Ladoo, Peanut Ladoo, Jaggery rice, Pasi Paruppu Payasam, Banana Appam etc.
Conclusion
Jaggery is a natural sweetener and a common sugar substitute that is popularly used in several parts of India. It is mainly produced by processing sugarcane juice or from palm tree sap and contains sucrose, fructose and some vitamins and minerals. This may be a reason why many believe jaggery to be a sugar replacement, however, jaggery is high in calories and still a form of sugar, so it’s best to use it in moderation. For diabetics trying to replace sugar, first consult with your healthcare professionals and find the healthiest option for you!
For such informative articles on health, nutrition and ageing, explore Right Shift. We’re community full of cheerleaders trying to motivate you to prioritise your health in your midlife. We have free tools like our health score calculator and free meal plan creator to get you started on this journey. Simply fill out your details to understand where your current health stands and then get a personalized meal plan according to your preferences and health goals. Start your wellness journey today by exploring tailored solutions on the Shift Shop, including wholesome products like jaggery oats cookies that support your health objectives.
Other Popular Blogs
Jaggery nutritional value | Different ways of using jaggery | Reducing cholesterol naturally | Foods that have healthy fats | Best cooking oil for good health |
FAQs
Eating jaggery in moderation every day can be beneficial due to its rich mineral content and its ability to aid digestion. However, consuming it in excess could lead to weight gain and fluctuating blood sugar levels.
While there are some jaggery health benefits, it might not be suitable for everyone. People with diabetes or those trying to lose weight should limit their intake as jaggery is high in calories and can increase blood sugar levels.