What is Vitamin A and What Are Its Major Functions As We Grow?
Blogs09 Jun 2025
IN THIS ARTICLE
Vitamin A is an important fat-soluble vitamin found naturally in many foods. Vitamin A has two main derivatives, retinol and retinoic acid. This vitamin is known for helping vision, cell division, growth, reproduction, and immunity while also having antioxidant properties. Additionally, there are also pigments known as carotenoids that are responsible for the red, orange and yellow colours of some vegetables. These carotenoids when consumed can be converted to Vitamin A by our body too!
Sounds amazing right? Well, let’s find out more about this vitamin in this article. We’ll cover the role vitamin A plays in the body, food sources of vitamin A and the benefits it can provide to support healthy ageing.
What is Vitamin A?
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays several essential roles in the body. It is scientifically classified into two main types: preformed Vitamin A (retinol and retinyl esters) and provitamin A carotenoids (beta-carotene, alpha-carotene, and beta-cryptoxanthin).
The Function of Vitamin A
Here are some of the main advantages of Vitamin A in the body:
1.Prevents Vision Loss
Age-related macular degeneration or AMD is the loss of vision in older people. Genetics, oxidative stress and normal ageing are some factors that can cause AMD.9 Studies have found that by having supplements that contain Vitamin A or carotenoids with antioxidant functions, it may be possible to prevent or delay vision loss that comes with age.
2.Cell Growth
Vitamin A is important for the growth and development of many types of cells throughout our lives. It also plays an important role in the maintenance of our heart, lungs and other organs.
3.Supports Pregnancies
Vitamin A is also known help support pregnancies as well. Mothers who meet their daily vitamin A requirements will be able to not only stay healthy, but keep their foetuses healthy too and prevent deficiency and other health issues.
4.Supports Immune Function
Having a deficiency in Vitamin A can lead to immune impairment, making you susceptible to many diseases and health issues. It plays a role in the creation of B cells and T cells which are required for immune responses against diseases. With its antioxidant benefits, Vitamin A prevents oxidative stress and may help support immune function to keep other health conditions at bay.
5.Healthy skin and hair
Vitamin A, especially its derivative, retinol, has been a buzzword in the skincare industry for the past decade. Science has found that Vitamin A is good for skin and hair. Some studies have seen its positive effects on acne (due to its wound healing, and sebum-reducing effects) and signs of ageing (due to promotion of new cell growth). Too little of this nutrient and too much can both be harmful to your skin and health, so practise caution and only have what is required!
6.Boosts Bone Health
Vitamin A may support bone health as well. Studies have found that those deficient in this vitamin are more likely to face fractures, especially hip fractures and that higher levels of Vitamin A were associated with lower risks. Overall, this vitamin has been recognised as an important factor in the development and maintenance of bone mass, so make sure to get your fill of this micronutrient for supporting your bones too!
Importance of Vitamin A as We Age
A Vitamin A deficiency is common in developing countries especially in younger children and pregnant or lactating women. Another group that is in danger of a deficiency is anyone facing health conditions such as cystic fibrosis and those with gastrointestinal disorders. Maintaining adequate Vitamin A intake can prevent age-related macular degeneration, support the immune system and prevent or reduce oxidative stress which can in turn reduce the risk of chronic health conditions such as obesity and diabetes etc.
How Much Vitamin A Do We Need?
The recommended daily intake (RDI) of Vitamin A for adults, according to the ICMR and the National Institute of Nutrition (NIN), is 1000 micrograms (mcg) for men and 840 (mcg) for women. This intake can be achieved through a balanced diet that includes a variety of Vitamin A-rich foods.
What are the Sources of Vitamin A?
To meet the recommended daily intake of Vitamin A, it is essential to include a variety of food sources in your diet. Some excellent sources of preformed Vitamin A (retinol) include:
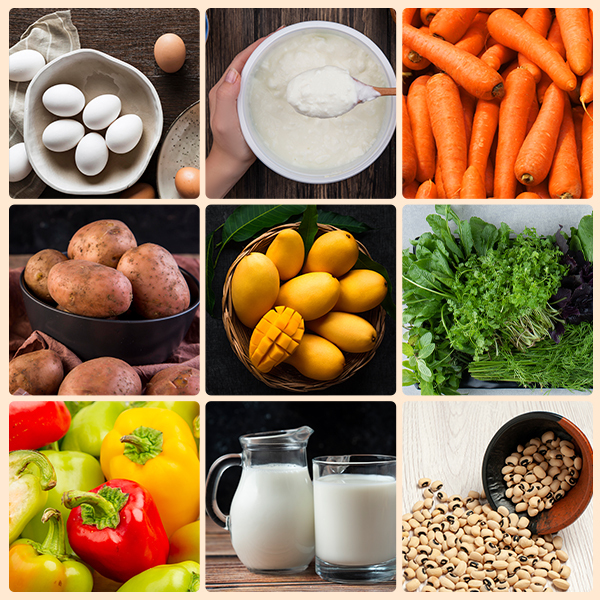

- Spinach
- Carrots
- Milk, cheese and yoghurt
- Bell peppers
- Mangoes
- Fortified breakfast cereals
- Eggs
- Black-eyed peas
- Broccoli
Including a mix of these foods in your diet can help ensure optimal Vitamin A intake, supporting overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
In short, Vitamin A is a helpful micronutrient that offers several health benefits for all age groups. It can help prevent age-related vision loss, support immunity, help in cell growth and promote bone health as well. Some benefits of Vitamin A also extend to healthy skin and hair, making it a crucial micronutrient to add to your life. Hence, understanding the function of Vitamin A and ensuring adequate intake is vital for maintaining overall health as we age. By incorporating a variety of Vitamin A-rich foods into your diet, you can enjoy the numerous benefits of this essential nutrient. Practice caution with your daily recommended Vitamin A intake and make sure to seek professional guidance when required.
Let RightShift be your companion in this journey, helping you make informed choices and supporting your overall health and well-being. Our trove of informational articles can help expand your knowledge on nutrition, health and ageing. Meanwhile, you can also try out our free health score calculator to understand your current health status and make immediate changes by trying our free meal plan creator as well! Try them now and make the right shift today!
Other Popular Blogs
Functioning of Vitamn K | Vitamin D Deficiency | Low Calorie Indian Foods | Foods For Muscle Gain | Vitamin B Benefits
FAQs
Vision issues like night blindness and respiratory issues are signs of a vitamin A deficiency.
Eggs, milk, cheese, yoghurt and liver are high in Vitamin A. Green leafy vegetables, carrots, and sweet potatoes are sources of provitamin A carotenoids which get converted into vitamin A.
The ICMR and the National Institute of Nutrition (NIN) recommend 1000 micrograms (mcg) of Vitamin A for men and 840 (mcg) for women.